What happened to getInitialProps
Remember getInitialProps?
Next.js has become more and more flexible over time.
Originally, getInitialProps was the only native data fetching method in Next.js.
Now, we've got:
getStaticPropsgetStaticPathsgetServerSideProps
So why did Next.js add these new methods, and why is getInitialProps not used as frequently anymore? Let's look at some of the reasons.
How does getInitialProps work?
On the server
On the initial request, getInitialProps is called on the server. This data is used to populate the server-side rendered document. Developers would assume it's safe to make API calls using API keys, call secure endpoints, and read from environment variables here, though that's largely not the case.
On the client
Why? Because as soon as the client takes over, getInitialProps will be called when you navigate to a new page. This code runs in the browser, meaning you wouldn't want to ship secrets to make those same API calls.
Example
Page.getInitialProps = async (ctx) => {
const res = await fetch('https://api.github.com/repos/vercel/next.js')
const json = await res.json()
return { stars: json.stargazers_count }
}
No harm here, right? This can run on both the server and the client without issue.
But what if we call an API that requires an API key?
const isServer = typeof window === 'undefined'
Page.getInitialProps = async (ctx) => {
if (isServer) {
const res = await fetch('https://example.com/secret-api-call', {
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${process.env.SECRET_API_KEY}`
}
})
const json = await res.json()
return { data: json.secret }
} else {
return { data: 'Not safe to call on the client' }
}
}
Do we see any problems here? The answer is yes. Our SECRET_API_KEY will be leaked to the client in this case.
This also leads to performance issues. If we include server-only modules not meant for the client, we can end up shipping massive JS bundles for no reason.
getInitialProps is a Swiss Army Knife of Next.js data fetching. Instead of being a generalist, let's reach for the right tool for the job.
What to do instead?
If you're using getInitialProps, what's your path forward? If you needed server-side rendering, what are the options?
Introducing getStaticProps & getStaticPaths
First things first, let's verify that you need server-side rendering. Lots of applications think SSR is required, but it's not. What's the alternative? Static rendering.
In Next.js, you can use getStaticProps and getStaticPaths to render static parts of your app.
getStaticPathsis used to generate a list of pages that your app should serve.getStaticPropsis used to fetch data for that specific page.
While this isn't a great metaphor, think of getStaticPaths as creating a bunch of buckets for your app to fill. getStaticProps is called for each bucket, and you can use it to fill that bucket with specific data it needs.
Consider a company's blog as an example of a type of page that works great for static generation. You want to generate a list of all the blog posts and fetch the content for each blog post.
In this case, getStaticPaths would return a list of all the blog posts, and getStaticProps would return the content for each blog post.
But what if the content in the CMS changes?
Perfect, you discovered the use case Incremental Static Regeneration (ISR).
Instead of generating all the pages and fetching content at build time, you can fetch it at runtime.
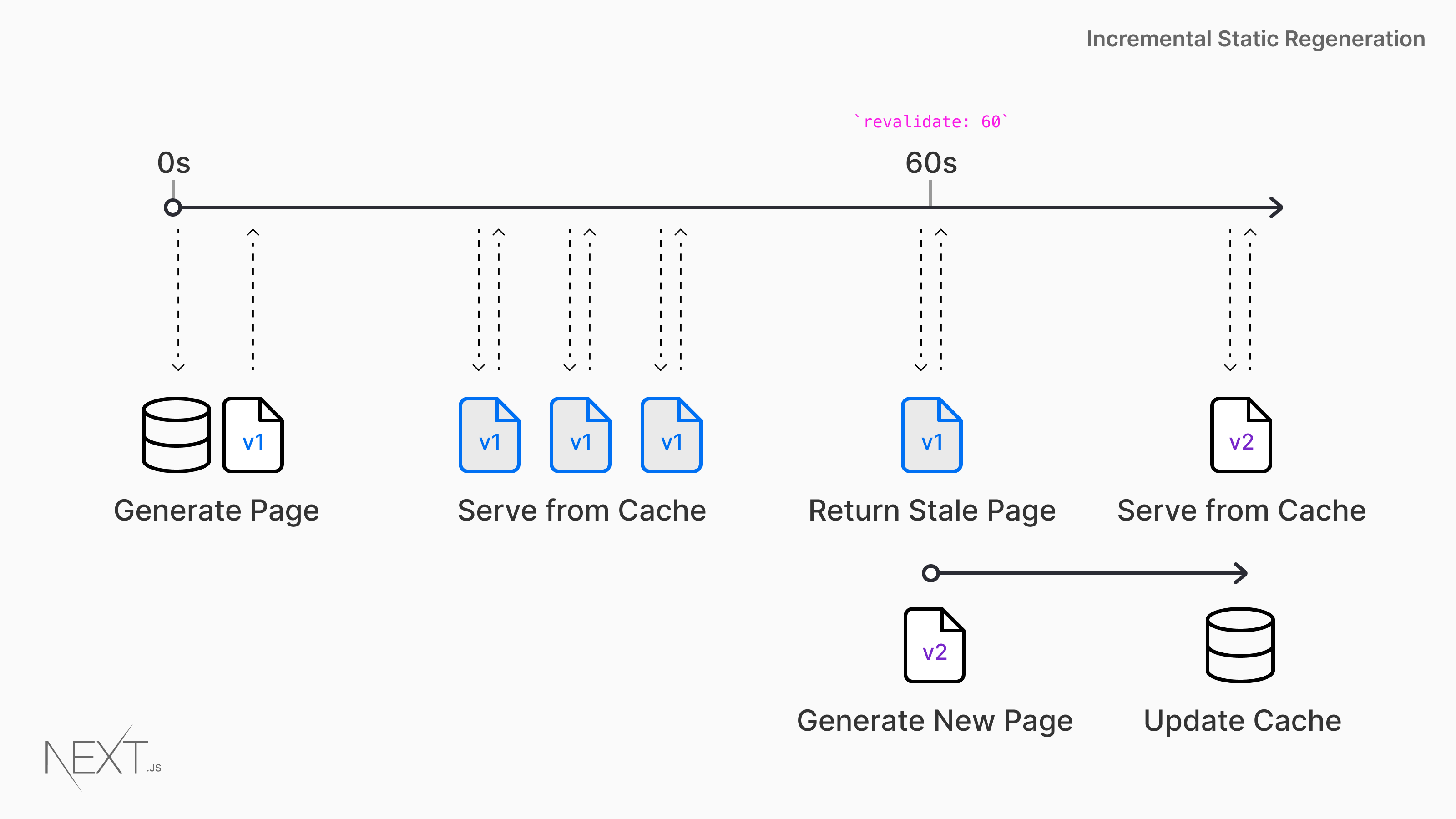
Use the getStaticPaths function, but specify a revalidate parameter to tell Next.js to re-generate the page when the data changes and the time expires.
This is a common pattern in web development called stale-while-revalidate.
We immediately serve the stale page to the user and update it with the new data as it's ready.
Really need SSR? getServerSideProps is your friend
If you're confident that you need SSR and that ISR will not work for you, you can use getServerSideProps to fetch data for the server-side rendered page.
This will be called for each incoming request, and you can use it to fetch data for the server-side rendered page.
If using this approach, I'd recommend you set some caching headers on the response, so you're not burning through serverless compute time.
Do I have to upgrade?
The quick answer: no. Next.js has phenomenal backward compatibility across versions. Are there still valid use cases for getInitialProps? 100% yes. There are cases where grabbing Swiss Army Knife makes sense and cases where getInitialProps is a good fit.
Best of luck building your Next.js app!
See you on the other side,
Drew
